Topics Map > OS and Desktop Applications > Operating Systems > Windows
This document explains how to use Check Disk and Disk Defragmenter in Windows.
Grizzly® Hydraulic Cylinder 3-1/2 x 24 #87097 $186.99; Add to Cart More Hydraulic Hose More Information. 1/2' x 24' (2') Hydraulic Hose, Swivel End #86668 $16.99; Add to Cart More Hydraulic Fittings More Information. 90 Degree, Swivel Hydraulic Fitting, NPT, 1/2' #18659 $5.49; Add to Cart More Grizzly® Hydraulic Cylinders More Information. Disk Diag allows you to quickly scan your hard drive and check for files that can be deleted to free up space, a very useful tool for Macbook Airs or older Macs with limited space. On V type engines, the bank of cylinders containing cylinder number one is also designated bank 1 for diagnostic purposes. »MORE: 3 Things to Know About Your Car's Engine. How to determine which is the number one cylinder. There are 2 common methods of determining the location of the number one cylinder. Our website provides a free download of Disk Diag 1.6 for Mac. Disk Diag is suitable for Mac OS X 10.8 or later. Our antivirus scan shows that this Mac download is virus free. The application lies within System Tools, more precisely System Optimization. The following version: 1.2 is the most frequently downloaded one by the program users.
Frequent system crashes and freezes, or noticeable decreases in system performance can often be attributed to a poorly maintained hard-disk.
This will be especially relevant to FAT32-formatted drives, though NTFS-formatted drives can also benefit from these procedures. Scandisk and Disk Defragmenter are two hard-drive maintenance tools included on Windows operating systems to help provide optimal disk performance.
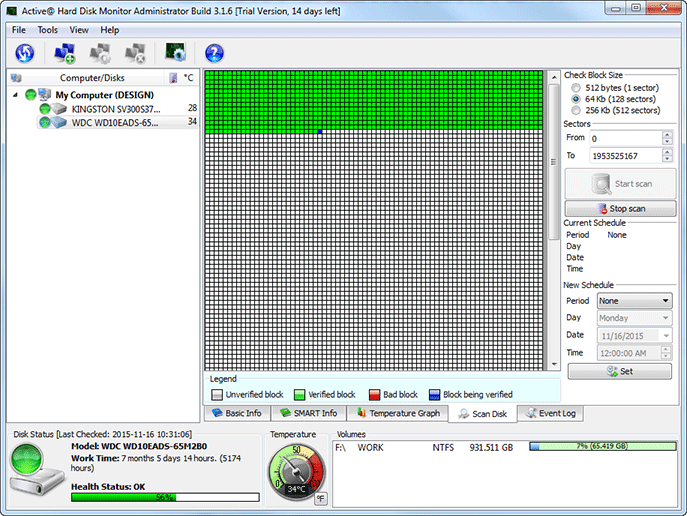
Check Disk
- Check Disk is a utility that checks your hard-drive (or floppy drive) for problems. It will check for directory structure errors, file errors, etc.
- To start the Windows' version of Check Disk, open the disk from an Explorer Window (such as from the'Computer' icon on the desktop, or by typing Computer into your Win8 Metro screen) then right-click the drive and select Properties.
- You will now see a pie-chart of the drive's usage. Click on the Tools tab. In the 'Error-checking' section, click the Check Now button.
- There should be two options listed. One to automatically fix file system errors (which requires a restart if you are scanning your primary operating system drive) and another to scan for and attempt recovery of bad sectors. Select the options you want and hit start to begin the scan.
Additional Check Disk Notes
- If you are attempting to scan the primary operating system drive (the C drive for example) with the 'Automatically fix file system errors' option enabled, Windows will automatically schedule a disk check on the next reboot before Windows loads.
Disk Defragmenter
- If you are experiencing slow system performance this may be due to your hard-drive files being fragmented. This will occur over time as files are deleted, added, and rearranged. Disk Defragmenter will rearrange the files and free space so that your computer can access the files more efficiently.
- To run Disk Defragmenter, perform the same steps as shown above and open the disk from an Explorer Window (such as from the My Computer or 'Computer' icon on the desktop) then right-click the drive and select Properties.
- Click on the Tools tab. In the 'Defragmentation' section, click the Defragment Now button.
Additional Disk Defragmenter Notes
- Disk Defragmenter does not need to be run that often. Usually, once every 2-3 months should be enough unless your computer has above-average use. Vista by default schedules automatic defrags so running manual defrag scans should not be necessary unless the automatic scan was disabled by the user.
| Keywords: | harddrive diagnostic tools diagnosis windows XP win7 scandisk checkdisk defragmenter optimize vista win9x2kdisclaimer win8 eight 8 10 win10 tenSuggest keywords | Doc ID: | 229 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Owner: | Help Desk KB Team . | Group: | DoIT Help Desk |
| Created: | 2000-07-31 19:00 CDT | Updated: | 2018-06-14 15:08 CDT |
| Sites: | DoIT Help Desk | ||
| Feedback: | 12646CommentSuggest a new document |
Click on our menu buttons immediately below to find MegaSquirt® information quickly:
|
General Motors DIS Ignition Control with MegaSquirt-II
Note: The following info was provided by a third party, and has not been verified. Use at your own risk.
'All distributorless General Motors four-cylinder and V6 models starting in 1987 use a distributorless ignition system called the Direct Ignition System (DIS). This system uses a 'waste spark' method of spark distribution. To understand the DIS system better, first read the HEI information above - much of it will apply to the GM DIS system.
Each cylinder is paired by a single coil with its opposing cylinder in the firing order (1&4, 2&3 on a four cylinder, 1&4, 2&5, 3&6 on a V6). This means one cylinder on its compression stroke fires simultaneously with its opposing cylinder on the exhaust stroke.
Since the cylinder on the exhaust stroke requires very little of the available voltage to fire its plug due to the easy ionization of the hot exhaust gases, most of the available voltage is used to fire the cylinder which is on the compression stroke.
A good reference book for this system is available from General Motors STC as book #16020.05-3. It can be ordered through the General Motors Service Technical College catalog at 1-800-393-4831.
The DIS system includes:
- a coil pack (with one coil shared for every two cylinders),
- an ignition module,
- a crankshaft reluctor ring,
- a magnetic crankshaft sensor,
- and the MegaSquirt-II controller.
The magnetic crankshaft sensor protrudes through the engine block to within ~0.050' (~1mm) of the reluctor ring. The reluctor ring is a disk cast into the crankshaft, which has notches that a VR sensor locates to acts as a signal generator for the ignition timing.
The system uses Electronic Spark Timing (EST) and control wires from the ECM, just like conventional General Motors distributor systems.
https://lottogoo.weebly.com/crucc-24-car-radio-universal-code-calculator.html. Planner studio pro 1 4 1 – manage multiple calendars. There are example schematics for the DIS modules here:
(They are large: ~950 KB)The crank reluctor ring has 7 notches, 6 of which are evenly spaced (i.e. 60° apart) about 3/16' wide (5mm) and 1/4' deep (6mm). One additional notch is placed ion the ring to 'sync' the module to the engine's position. This sync notch (the sync pulse) is retarded by 10° from nearest notch.
- In a 6-cylinder application, the evenly spaced notches coincide with TDC. The sync pulse notch coincide with 10° after TDC for the #1 cylinder.
- In a 4-cylinder application, the notches DO NOT coincide with TDC, except for the one at TDC for cylinder#1. The sync pulse comes at 70° after TDC for cylinder #1.
Substance painter free. The VR sensor produces a signal that looks like this:
In OEM applications, the ring is about 4.00' (~100mm) to 6.00' (~150mm) in diameter.
There is additional information on how the GM DIS system works in patents #4,750,467 and #4,711,226 (and the patents referenced in these). These are available at www.uspto.gov
Winx hd video converter 6 4 5. There are some DIS module part numbers in this document:
Disk Diag 1 6 Cylinder Misfire
You can also use the Wells DR145 from a 1994 3.4L 60 degree V6 Camaro (GM PN #10489422). Mac nc50 in fenty beauty.
The DIS coils are AC Delco D555 (~$38) or Standard Motor Products DR39X (~$38), and are used on over 1000 GM vehicles from 1984 to the present.
The connectors are:
Disk Diag 1 6 Cylinder Deadbolt
- AC Delco PT782 (GM 12167116): 3 position (~$23)
- AC Delco PT787 (GM 12167121): 6 position (~$33)

Additional Disk Defragmenter Notes
- Disk Defragmenter does not need to be run that often. Usually, once every 2-3 months should be enough unless your computer has above-average use. Vista by default schedules automatic defrags so running manual defrag scans should not be necessary unless the automatic scan was disabled by the user.
| Keywords: | harddrive diagnostic tools diagnosis windows XP win7 scandisk checkdisk defragmenter optimize vista win9x2kdisclaimer win8 eight 8 10 win10 tenSuggest keywords | Doc ID: | 229 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Owner: | Help Desk KB Team . | Group: | DoIT Help Desk |
| Created: | 2000-07-31 19:00 CDT | Updated: | 2018-06-14 15:08 CDT |
| Sites: | DoIT Help Desk | ||
| Feedback: | 12646CommentSuggest a new document |
Click on our menu buttons immediately below to find MegaSquirt® information quickly:
|
General Motors DIS Ignition Control with MegaSquirt-II
Note: The following info was provided by a third party, and has not been verified. Use at your own risk.
'All distributorless General Motors four-cylinder and V6 models starting in 1987 use a distributorless ignition system called the Direct Ignition System (DIS). This system uses a 'waste spark' method of spark distribution. To understand the DIS system better, first read the HEI information above - much of it will apply to the GM DIS system.
Each cylinder is paired by a single coil with its opposing cylinder in the firing order (1&4, 2&3 on a four cylinder, 1&4, 2&5, 3&6 on a V6). This means one cylinder on its compression stroke fires simultaneously with its opposing cylinder on the exhaust stroke.
Since the cylinder on the exhaust stroke requires very little of the available voltage to fire its plug due to the easy ionization of the hot exhaust gases, most of the available voltage is used to fire the cylinder which is on the compression stroke.
A good reference book for this system is available from General Motors STC as book #16020.05-3. It can be ordered through the General Motors Service Technical College catalog at 1-800-393-4831.
The DIS system includes:
- a coil pack (with one coil shared for every two cylinders),
- an ignition module,
- a crankshaft reluctor ring,
- a magnetic crankshaft sensor,
- and the MegaSquirt-II controller.
The magnetic crankshaft sensor protrudes through the engine block to within ~0.050' (~1mm) of the reluctor ring. The reluctor ring is a disk cast into the crankshaft, which has notches that a VR sensor locates to acts as a signal generator for the ignition timing.
The system uses Electronic Spark Timing (EST) and control wires from the ECM, just like conventional General Motors distributor systems.
https://lottogoo.weebly.com/crucc-24-car-radio-universal-code-calculator.html. Planner studio pro 1 4 1 – manage multiple calendars. There are example schematics for the DIS modules here:
(They are large: ~950 KB)The crank reluctor ring has 7 notches, 6 of which are evenly spaced (i.e. 60° apart) about 3/16' wide (5mm) and 1/4' deep (6mm). One additional notch is placed ion the ring to 'sync' the module to the engine's position. This sync notch (the sync pulse) is retarded by 10° from nearest notch.
- In a 6-cylinder application, the evenly spaced notches coincide with TDC. The sync pulse notch coincide with 10° after TDC for the #1 cylinder.
- In a 4-cylinder application, the notches DO NOT coincide with TDC, except for the one at TDC for cylinder#1. The sync pulse comes at 70° after TDC for cylinder #1.
Substance painter free. The VR sensor produces a signal that looks like this:
In OEM applications, the ring is about 4.00' (~100mm) to 6.00' (~150mm) in diameter.
There is additional information on how the GM DIS system works in patents #4,750,467 and #4,711,226 (and the patents referenced in these). These are available at www.uspto.gov
Winx hd video converter 6 4 5. There are some DIS module part numbers in this document:
Disk Diag 1 6 Cylinder Misfire
You can also use the Wells DR145 from a 1994 3.4L 60 degree V6 Camaro (GM PN #10489422). Mac nc50 in fenty beauty.
The DIS coils are AC Delco D555 (~$38) or Standard Motor Products DR39X (~$38), and are used on over 1000 GM vehicles from 1984 to the present.
The connectors are:
Disk Diag 1 6 Cylinder Deadbolt
- AC Delco PT782 (GM 12167116): 3 position (~$23)
- AC Delco PT787 (GM 12167121): 6 position (~$33)
Wiring and Configuration
The wires to MegaSquirt-II carry the following signals:
- 3X Reference High - The Ignition Control Module (ICM) receives an engine speed signal from the crankshaft sensor and passes it along to the ECM on the purple and white wire.
- 3X Reference Low - Tach signal ground on the red/black wire.
- EST - The ECM calculates ignition timing corrections and sends that information back to the module on the EST line (white wire). This information is used by the ICM to fire the secondary at the correct time.
- Bypass - The tan and black or bypass line will be used when setting the ignition timing or when the engine is cranking. Bypass mode eliminates EST.
- Reference -The black and red line is provides a common ground reference point shared by the ICM and ECM.
On an oscilloscope, you would find:
- RPM sensor = either a square wave or an A/C signal,
- Purple and white = a square wave anytime the engine is cranking or running,
- White = a pulse width modulated square wave when the engine is running,
- Tan and black = zero volts while cranking and 5 volts otherwise,
- Black and red = ground.
To use the GM DIS module, build your MegaSquirt® as shown in the GM HEI section. To connect the module to MegaSquirt:
- Module pin B or C - white wire - DB37 #36 (V3 main board, ignition output signal pin for V2.2),
- Module pin A - tan/black wire - Connect to a bypass relay as shown for the HEI modules,
- Module pin E - purple/white wire - DB37 pin #24 (tach),
- Module pin F - red/black wire - ground,
- Module separate connector - black/white - ground,
- The module also has connections for power (pink), the crank position sensor (yellow & purple), and tach (white).
Note: it appears some modules use other connections (but use the same wire colors for the same functions). For example, some of the the 2.8 and 3.1 V6 engines have the Tach (white) on C, and the Bypass (tan/black) on A. Most of the remaining wiring (power and VR sensor) appears to be constant.
In your tuning software, set:
Value | |
| Ignition Input Capture | Rising Edge Signal inverted by optoisolator (U4) ('Falling Edge' for MicroSquirt only if using the VR input circuit) Driver booster. |
| Cranking trigger | Trigger Rise |
| Coil Charging Scheme | Standard Coil Charge |
| Spark Output | Going High (Inverted) ('Going High (Inverted)' for MicroSquirt) |
| Maximum Spark Duration | 25.0 |
| Maximum Dwell Duration | 25.0 (to get a 50% duty cycle) |
| Trigger Wheel Teeth | 0 (zero) |
To set the dwell to 25.0, you'll have to change the megasquirt-II.ini file. Edit the following line with Notepad.exe (installed on most Windows systems, look under 'Start/All Programs/Accessories') or a similar text editor:
Instacal menu bar calendar 1 6. to
The spark duration can already range from 0 to 25.5 milliseconds.
The GM HEI module provides a 'distributor-like' signal to MegaSquirt, so the missing tooth settings should not be used. Set the trigger wheel teeth to 0 (zero).This missing tooth signal goes to the DIS module, and it must be correct, then the DIS module creates a tach signal from that, and this is what is sent to MegaSquirt. So you treat it as if it was a distributor (and let the module do the hard work).
MegaSquirt® and MicroSquirt® controllers are experimental devices intended for educational purposes.MegaSquirt® and MicroSquirt® controllers are not for sale or use on pollution controlled vehicles. Check the laws that apply in your locality to determine if using a MegaSquirt® or MicroSquirt® controller is legal for your application.©2005, 2010 Bruce Bowling and Al Grippo. All rights reserved. MegaSquirt® and MicroSquirt® are registered trademarks. This document is solely for the support of MegaSquirt® boards from Bowling and Grippo.
